

The well was drilled successfully using managed pressure drilling techniques, allowing for visibility of the productive intervals throughout the drilling process in the Austin Chalk. The JV is currently working towards setting a production packer and production tubing to complete the well as an open hole Austin Chalk producer.
#Drilling hydraulics program full#
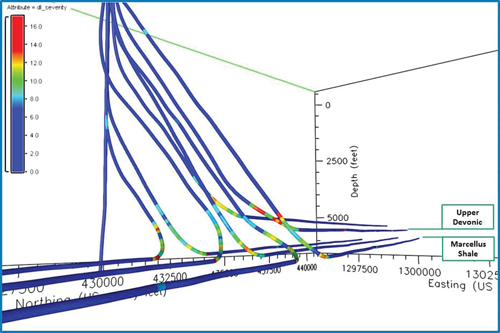
On February 14, 2021, the JV reached its second milestone, with the conclusion of its drilling of its lateral with a full vertical section distance of 4,046 feet. On February 13, 2021, the drilling had reached its first milestone which initiated a contractual vesting of asset assignments with the successful drilling of a minimum lateral distance of 2,500 feet. The JV commenced active drilling on Januand on Januthe drilling reached its targeted location in the Austin Chalk formation. Based on extensive survey and planning work, combined with the completion techniques employed, the JV anticipates achieving attractive economics at approximately 50% of the cost of a similar-sized traditional hydraulic fracturing program. Following its robust planning program, the JV commenced a unique drilling project in January 2021 focused on the drilling of a directional oil well in a targeted portion of the Austin Chalk formation. (“Blackbrush”) and GeoTerre, LLC (“GeoTerre”) announced in October 2020.ĭuring the quarter ended December 31, 2020, the JV executed the planning phase for its first major drilling project, while simultaneously acquiring additional mineral lease rights contiguous to the originally acquired leasehold and 3D seismic survey results in Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana. ("Ecoark" or the “Company”) (OTC: ZEST), is providing the following updates regarding the Company’s joint drilling venture (the “JV”) with BlackBrush Oil & Gas, L.P. 16, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) - Ecoark Holdings, Inc. It is affected by the drilling fluid properties and geometry (configuration) of the circulating system.SAN ANTONIO, Feb. Rotary drilling hydraulics is concerned with proper utilization of the drilling fluid pump horsepower. It affects mud circulation, hole-cleaning efficiency, cementing, rate of penetration (ROP), and hence total drilling time and cost. An efficient hydraulics system is a prerequisite to the success of any drilling and completions operation. Drilling is the art and science of making boreholes for hydrocarbon production, in a manner that is safe, economic, and environmentally responsible. The dynamic state deals with the fluid movement, pipe movement, and cutting transport. The hydraulic system is the drilling fluid system in the wellbore when the fluid is in static or dynamic state. Proper design and maintenance of this system increases drilling efficiency (high rate of penetration) and lowers the overall drilling cost.
Hydraulics system plays an important role during rotary drilling operations. A user-friendly computer program was written to facilitate repeated analyses using any combination of rheological model and equivalent annular diameter definitions for the conventional drilling fluids for all ranges of inclination using the Rudi Rubiandini’s cuttings transport model.
The impacts of rheological models and equivalent annular diameter definitions on annular pressure loss and ECD were examined for the conventional drilling fluids while aluminium oxide nanoparticles were used to examine the influence of nanofluids on the annular pressure gradient and ECD. They possess unique characteristics that differentiate them from microparticles, and make them adaptable to a wide range of applications. The nanoparticles are particles with an average diameter of less than 100nm. Nanofluids are specialized fluids obtained by careful combination of nanoparticles and a base fluid. This thesis examines hydraulics optimization using conventional drilling fluids and nano-based drilling fluids.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
